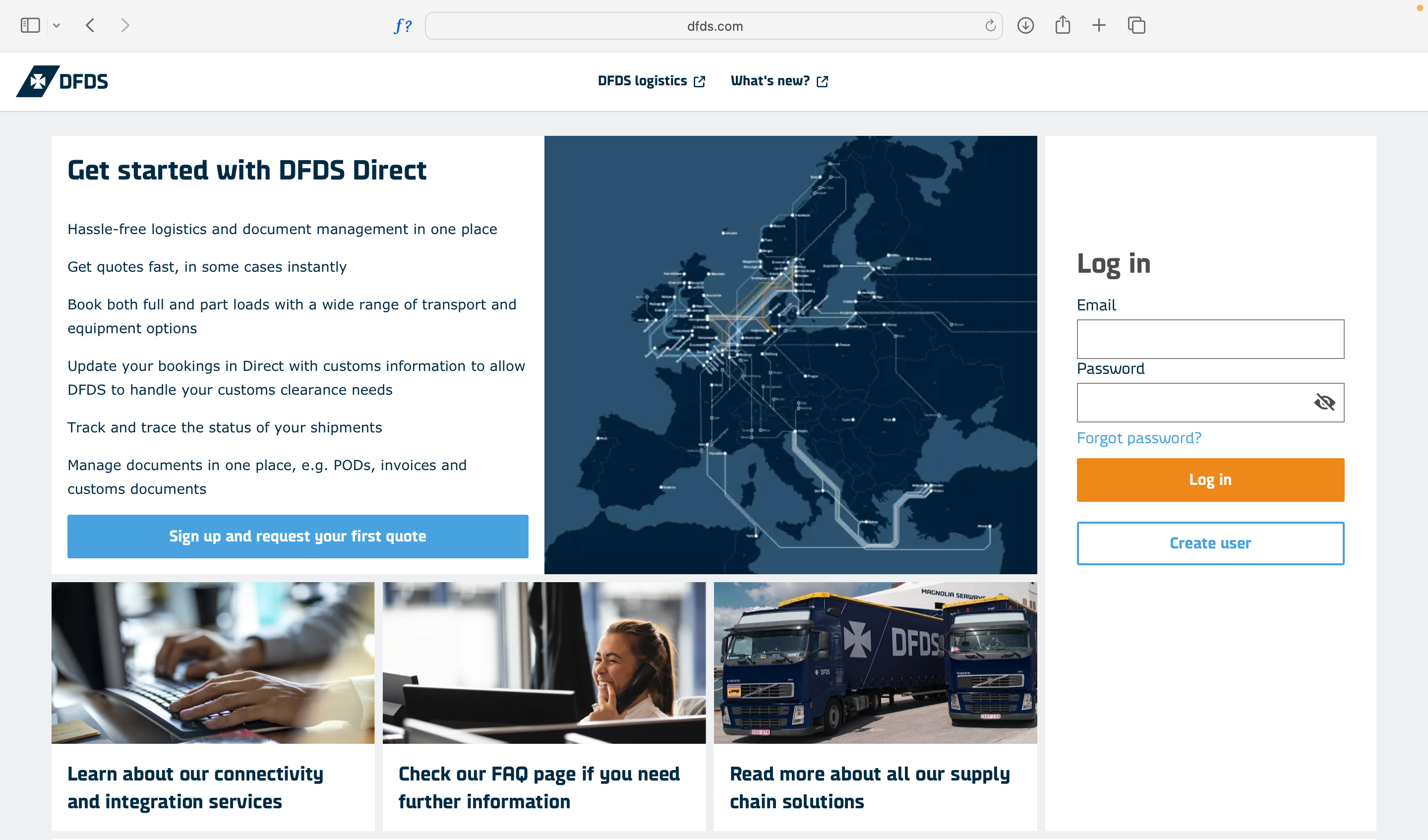
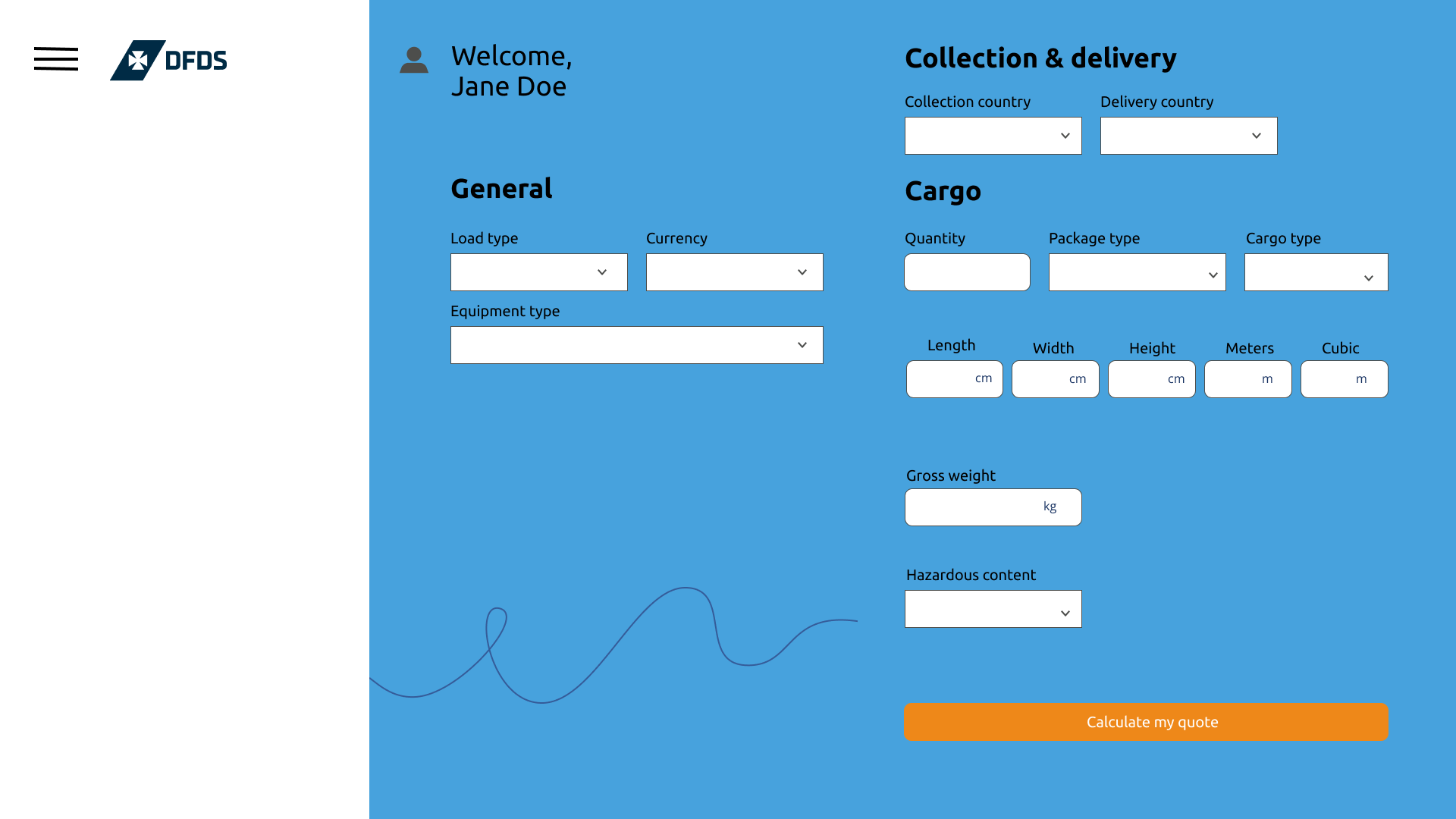
Onboarding Screens (desktop design)



The objective of this case was to showcase process-oriented approach to tasks and problem-solving skills.
Task
Improving Conversion in DFDS Direct. Improve conversion in DFDS Direct, an online solution for companies transporting goods globally. Users primarily seek quotes for specific transports but the onboarding flow requires enhancement to increase quote requests.
Goal
Increase the number of users submitting the quote form by optimizing the “New Spot Quote” button on the last step of the onboarding flow.
Follow out a systematic process that involves understanding the current onboarding flow, identifying pain points, ideating potential solutions, and validating those solutions through (hypothetical) testing.
The following steps outline this process
- Research & Analysis
- Study the existing onboarding flow in DFDS Direct, including the user journey, touchpoints, and key conversion steps.
- Collect data on user behavior, such as drop-off points and exit rates, to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Conduct user interviews or surveys to gather qualitative insights and understand user motivations, needs, and pain points during the onboarding process.
- Identify Key Issues
- Analyze the research findings to pinpoint the main obstacles preventing users from requesting quotes.
- Identify any usability issues, confusion, or friction points that may deter users from reaching the final step.
- Ideation & Solution Generation
- Brainstorm potential solutions to address the identified issues.
- Sketch out different design concepts and variations that focus on optimizing the “New Spot Quote” button and enhancing the user experience.
- Consider factors such as clarity of information, visual hierarchy, persuasive design techniques, and minimizing friction during the onboarding process.
- Design & Prototyping
- Select the most promising design concepts from the ideation phase.
- Create low or high fidelity prototypes that showcase the proposed changes.
- Iteratively refine the designs to ensure they effectively guide users towards the desired action of submitting the quote form.
#2 Low or High Fidelity Design
These are some changes that can be made to the pages and/or flows along with their expected impact:
- Simplify and Clarify Information
- Streamline the onboarding flow by eliminating unnecessary steps and reducing cognitive load.
- Provide clear instructions and tooltips to guide users through the process.
- Use visual cues, such as progress indicators, to indicate the user’s position in the flow.
- Highlight Benefits & Value Proposition
- Communicate the unique selling points and benefits of using DFDS Direct during the onboarding process.
- Incorporate persuasive copywriting and visuals to encourage users to request a quote.
- Display customer testimonials or success stories to build trust and credibility.
- Enhance Button Visibility and Placement
- Increase the visual prominence of the “New Spot Quote” button on the last step of the onboarding flow.
- Ensure the button stands out by using color contrast, size, or placement techniques.
- Optimize the button text to be action-oriented and compelling.
#3 Process Description for Testing Changes
To test these changes and ensure their effectiveness, the following methods can be followed:
- Usability Testing
- Recruit representative users who match the target audience and have not previously used DFDS Direct.
- Create a usability test plan outlining the tasks users need to complete.
- Observe users as they interact with the redesigned onboarding flow, collecting feedback and identifying any issues or confusion.
- Use tools like screen recording and think-aloud protocol to capture valuable insights.
- A/B Testing
- Conduct A/B testing to compare the performance of the original onboarding flow with the redesigned version.
- Randomly assign users to either the control group (existing flow) or the experimental.
